Our Department takes pride in effectively maintaining the roadways in your community in the most cost-effective, soundly engineered, and environmentally friendly manner. There are many types of pavement treatment options that apply to roads. We are moving forward with implementing sustainable treatments
A specific treatment depending on but not limited to the surface condition of the road, the condition of the underlying substructure, and the amount of traffic volume. Environmental, financial, and community considerations are also factors that are considered in selecting the right treatment.
Treatment TypesAs was mentioned in our Road Stewardship write-up we talked about performing the right treatment on the right road at the right time while building it the right way. We also mentioned how our Pavement Management System determines the pavement condition which greatly influences what treatment type to place on the roadway. Since 2008 our Department has evolved and changed our approach into treating our roads by implementing Pavement Preservation treatments – ensuring that the oxidized pavement is treated prior to pavement distresses are formed. More recently our approach has evolved even further as we implement Green Measures looking to ensure that we utilize sustainable treatments whenever possible.
Before presenting the treatment options understanding how a road is built and knowing what factors impact the road’s longevity are information that is helpful to getting an understanding of our Departments approach in treating our roads. The next two sections provide that information.
Road ComponentsA road can be broken down into three main layers or components: the top surface typically asphalt or concrete pavement; the second layer consisting of crushed rock called base; and then below that the native soil or the foundation. At times, the surface pavement is placed directly on the native soil. Each component plays an important role in the overall performance of the road. The surface layer provides the smooth riding surface that also provides the necessary skid resistance. Another important role of the top layer is to provide a protective layer preventing water from accessing the underlying base material and native soil. The base layer is the main structural element of the pavement and spreads the wheel loads so that the foundation is not overstressed. The native soil or foundation is the final layer where the load stress is transferred.
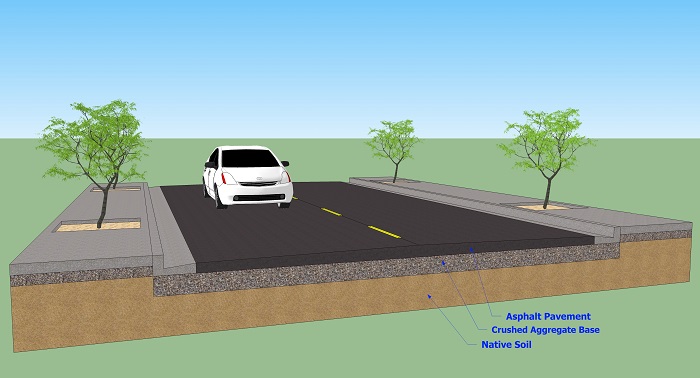
Factors that impact the performance of the roadAs pavement ages it starts to deteriorate. How quickly it breaks down is influenced by many factors. The primary factors are the environment and traffic loadings. Sunlight over time oxidizes the surface layer and causes it to become brittle. If the pavement is too brittle cracks start to form as a result from high repetitions of traffic loading on the pavement. If the pavement is not sealed properly, rainwater or irrigation water can infiltrate the cracks into the base layer and damage the structural integrity of the pavement. Water can erode or wash away the underlying base layers and cause the pavement to fail from lack of support.
The treatment types shown on this page are a compilation of the treatments that our Department has used in maintaining our roads.